Lay summary midterm review November 2022
At the time of the midterm review November 2022, progress was made at all levels. Several of the technologies dedicated for delivery of nucleic acids (NA; siRNA, mRNA, gapmer antisense oligonucleotides and miRNA) into the cells
to change their behaviour, showed efficiency. The PAA nanoparticles efficiently transfected cells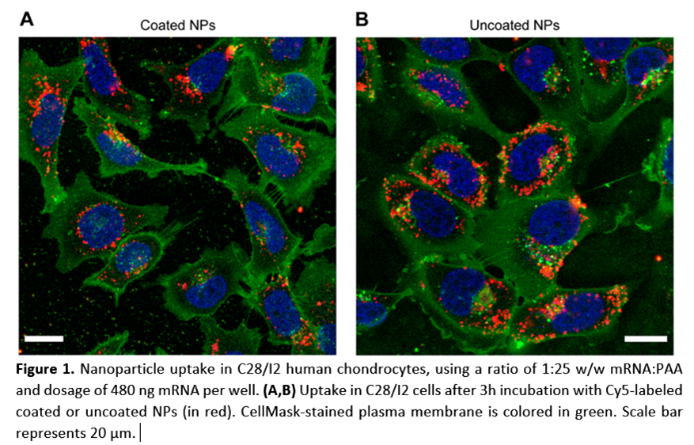 from cartilage (Fig 1), the synovial capsule and intervertebral disc cells and also transfected IVD cells in agarose gels as model for the IVD, demonstrating they entered the cells and released their NA cargo that then changed protein production. Polymers were synthesised at efficient yields to prepare dendriplexes with siRNA at the relevant size and charge. Albumin-NA assemblies incorporating antisense oligonucleotides have been produced, and albumin-NA complexes incorporated in microbubbles that can be used with ultrasound for more efficient cellular/tissue delivery. Additionally, novel hydrogels for delivery of NA, that can also carry cells to help regenerate the tissues, were developed. Efficient development and application of these carriers was supported by quality by design approaches (Fig 2). In addition, modified siRNAs were designed that more effect
from cartilage (Fig 1), the synovial capsule and intervertebral disc cells and also transfected IVD cells in agarose gels as model for the IVD, demonstrating they entered the cells and released their NA cargo that then changed protein production. Polymers were synthesised at efficient yields to prepare dendriplexes with siRNA at the relevant size and charge. Albumin-NA assemblies incorporating antisense oligonucleotides have been produced, and albumin-NA complexes incorporated in microbubbles that can be used with ultrasound for more efficient cellular/tissue delivery. Additionally, novel hydrogels for delivery of NA, that can also carry cells to help regenerate the tissues, were developed. Efficient development and application of these carriers was supported by quality by design approaches (Fig 2). In addition, modified siRNAs were designed that more effect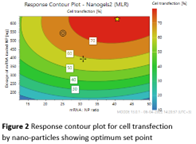 ively and selectively can inhibit the production of proteins, for example those that cause inflammation or breakdown of IVD or joint tissue. On the side of technologies that enhance the delivery to the tissues, targeting molecules have been incorporated in albumin (Fig 3), a serum protein that serves as natural carrier for several
ively and selectively can inhibit the production of proteins, for example those that cause inflammation or breakdown of IVD or joint tissue. On the side of technologies that enhance the delivery to the tissues, targeting molecules have been incorporated in albumin (Fig 3), a serum protein that serves as natural carrier for several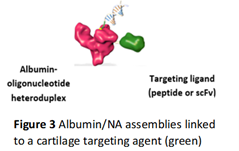 compounds in our body. Ultrasound technology enhanced penetration of model nanoparticles into agarose gels as tissue phantoms, which paves the way towards application in actual cartilage and IVD tissue. The complex tissue and organ ex vivo models used to test the effectivity and biological effects of the carrier-NA combinations were further optimised or tested for delivery for NAs. In an ex vivo joint model OA was successfully induced by enzymatic degradation. As a possible target in OA for the NAs, YAP was shown to be promising, inhibiting the negative response of tissue cells to inflammation. As tool to sensitively detect (small amounts of) newly made proteoglycans, essential compounds of the tissue, incorporation of novel click-chemistry labelled building blocks was shown in cartilage cells and tis
compounds in our body. Ultrasound technology enhanced penetration of model nanoparticles into agarose gels as tissue phantoms, which paves the way towards application in actual cartilage and IVD tissue. The complex tissue and organ ex vivo models used to test the effectivity and biological effects of the carrier-NA combinations were further optimised or tested for delivery for NAs. In an ex vivo joint model OA was successfully induced by enzymatic degradation. As a possible target in OA for the NAs, YAP was shown to be promising, inhibiting the negative response of tissue cells to inflammation. As tool to sensitively detect (small amounts of) newly made proteoglycans, essential compounds of the tissue, incorporation of novel click-chemistry labelled building blocks was shown in cartilage cells and tis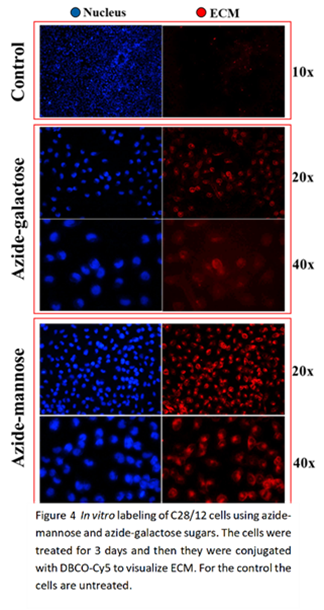 sues (Fig 4). Finally, we established an educational framework towards the integration of ethics, by incorporating early career researchers’ (ESRs) perceptions of the main ethical dimensions of their work and stimulating the reflection on these aspects. Given our involvement with sensitive data, animals, human cells, tissue, or body parts, we place a strong emphasis on addressing the ethical aspects of our research, identifying unwanted impacts on society We also discussed the responsible use of resources to minimize environmental impact and contribute to a sustainable future.
sues (Fig 4). Finally, we established an educational framework towards the integration of ethics, by incorporating early career researchers’ (ESRs) perceptions of the main ethical dimensions of their work and stimulating the reflection on these aspects. Given our involvement with sensitive data, animals, human cells, tissue, or body parts, we place a strong emphasis on addressing the ethical aspects of our research, identifying unwanted impacts on society We also discussed the responsible use of resources to minimize environmental impact and contribute to a sustainable future.

